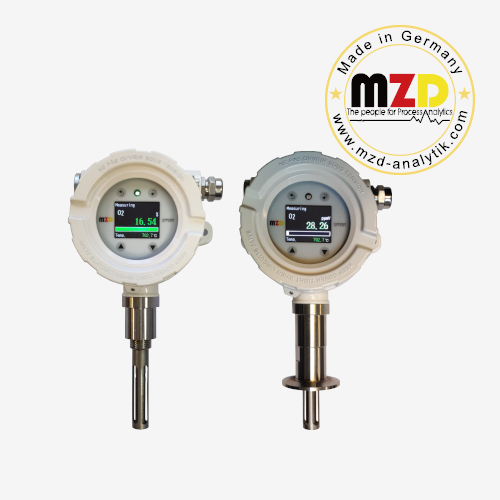

Description
SMART-OXZ Oxygen Analyzer uses a unique reference built-in zirconia technology, higher accuracy and repeatability oxygen measurement, no need to provide standard air and calibration. The sensor life is typically 5 years or more and is typically used for oxygen content measurements at ppb, ppm, air concentration (20.64%). The analyzer employs a Type B (Pt–Rh) thermocouple to measure the absolute temperature of the zirconia probe, which significantly enhances measurement stability, accuracy, and long-term reliability under high-temperature conditions.
Principle
Zirconia (ZrO2) is a ceramic, doped with a certain percentage of low-valent metal oxides as stabilizers, such as calcium oxide (CaO), magnesium oxide (MgO), and yttrium oxide (Y2O3), it has high-temperature conductivity, a conductor with ionic conductive properties, and becomes a zirconia solid electrolyte. At a certain temperature, when the oxygen content in the gas on both sides of the zirconia tube is different, a typical oxygen concentration difference cell is formed.
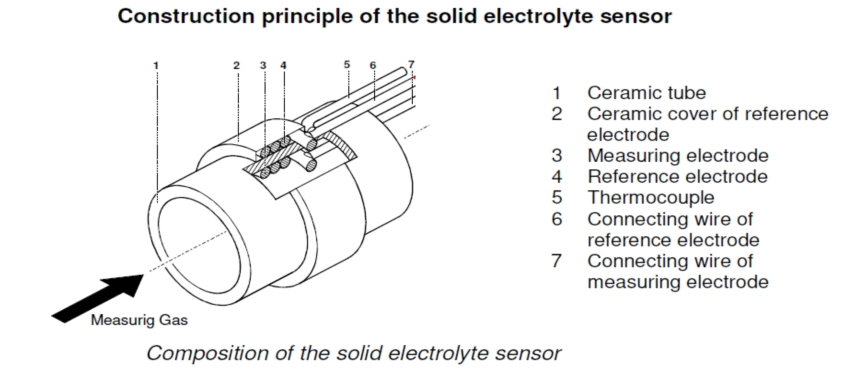
The zirconia tube as a whole is tubular, separated by zirconia material, and a porous layer of metal is sintered on each side of the zirconia as an electrode (usually Pt is used as the electrode material). At a certain temperature (600℃~1400℃), oxygen molecules on the side with higher oxygen content are adsorbed on the electrode, making the electrode on that side positively charged and the positive or anode of the oxygen concentration difference battery. Under the catalytic action of platinum, a reduction reaction occurs and electrons are obtained to form oxygen ions. The oxygen ions migrate through the holes in the zirconia crystal to the other side where the oxygen content is lower, making that electrode negatively charged and the negative or cathode of the oxygen concentration cell. At the platinum electrode electrons are lost and oxygen molecules are formed. This creates a certain potential at the two electrodes due to the buildup of positive and negative charges, which is related to the difference in oxygen content concentration in the two measured gases of zirconia, in accordance with Nernst equation:
E=(RT/4F)*Ln(P0/P)
Where
E------- oxygen concentration difference potential (mV)
R------- gas constant 8.3145 J/mol-K
T------- zirconia probe operating temperature (K, absolute temperature) = 273.15 + t (°C)
F------- Faraday constant, 96485.3365 (C/mol)
P0------- partial pressure of oxygen in the reference gas
P ------- Oxygen partial pressure in the sample gas
The oxygen partial pressure (P) in the gas to be measured can be calculated by measuring the concentration cell potential E and the absolute temperature of the zirconia probe, and thus the oxygen concentration in the gas to be measured.
Using a Type B thermocouple to measure T provides superior high-temperature stability, minimizes drift, and ensures accurate oxygen calculations over long-term operation, particularly in harsh or high-temperature industrial environments.
The zirconia method has high sensitivity, fast response time, wide linear range, good reproducibility and stability. The internal structure is simple and almost independent of external environmental conditions such as temperature, vibration, etc., and requires little maintenance. However, the zirconia method is not suitable for measuring oxygen concentration in reducing gases or gas samples with high reducing gas content because the oxygen concentration is affected by the reducing gas in the gas to be measured, resulting in low measurement results.
Main applications of zirconia analyzer:
1. inert gas measurement of trace oxygen content, electronic semiconductor industry, air separation, steel metallurgy, chemical fertilizer, chemical industry, welding protection, etc.
2. flue gas measurement of percent oxygen content, power plants, petrochemical refining, chemical industry, iron and steel metallurgy, cement and building materials, boilers, etc.
Using a Type B thermocouple to measure T provides superior high-temperature stability, minimizes drift, and ensures accurate oxygen calculations over long-term operation, particularly in harsh or high-temperature industrial environments.
Advantages of Type B Thermocouple
★High-temperature stability: Operates reliably at 600–1400℃ without degradation.
★Low drift: Ensures consistent oxygen readings over years of continuous operation.
★Trace oxygen measurement accuracy: Essential for ppb/ppm-level detection in protective or inert gases.
★Enhanced reliability: Reduces temperature-related measurement errors, improving repeatability and reproducibility.
Application
▲ASU(Air separation uint)
▲Fertilizer, Chemical, Pharmaceutical industry
▲Petroleum and Petrochemical industry
▲Semiconductor industry
▲Food and beverage industry
▲Metallurgical iron and steel industry
▲Nuclear,,heat treatment, welding protection
▲Aerospace and defense
▲Biological research
▲Light bulb manufacturing, semiconductor
▲Optical fiber research
▲Inert gas generator
▲Glass manufacturing
▲Special gas
▲Laboratory
▲Flare monitoring
▲Extraction and processing of natural gas
▲Environmental area monitoring
▲Anesthesia, breathing and prenatal care
Advantage
★Quick response
★High accuracy and repeatability
★No drift, maintenance-free, no calibration required*
★Rugged and durable design
★Easy installation
★Comfortable and friendly operation
★Long-life zirconia sensor
★Temperature measurement via Type B thermocouple ensures high stability and precise oxygen calculations
Features
• Quick and convenient
The English navigation menu can be operated easily.
• Process safety
1.8" color LCD screen, magnetic button operation and debugging
LED alarm(NAMUR NE107), clearly visible from long distances and in dark areas
Alarm immediately, safe the process
• Powerful self-diagnosis function
Built-in heartbeat monitoring function and watchdog
Monitor the status of transmitter and sensors, and promptly remind customers to take necessary maintenance
High-standard hardware and software security and password protection
• 2 Relays (2A, 230V AC/DC freely set alarm) and 1 Relay (System alarm)
• RS485 MODBUS communication
Technical Summary Table: Type B vs Type K Thermocouples
| Feature / Parameter | Type B (Pt–Rh) | Type K (NiCr–NiAl) | Engineering Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature Range | 500–1700 °C | −200–1260 °C | Type B suitable for high-temperature and extreme conditions; stable beyond Type K limits. |
| High-Temperature Stability / Long-Term Drift | Very low drift, high stability | Prone to oxidation and drift at high T | Type B ensures accurate long-term measurements. |
| Corrosion & Chemical Resistance | Platinum–rhodium resists oxidation and corrosion | Nickel-based alloys degrade in harsh atmospheres | Type B ideal for harsh industrial environments; reduces systematic errors. |
| Trace Oxygen / ppm / ppb Accuracy | High — temperature reference stable | Lower — drift increases measurement error | Type B supports precise trace oxygen monitoring. |
| Cost & System Complexity | Higher — Pt–Rh, compensation cables, precision electronics | Lower — simpler, inexpensive | Type B higher upfront cost but lower long-term maintenance. |
| Application Flexibility | Wide — single probe covers low to high temperature | Narrow — may need different probes per temperature | Type B simplifies probe selection, reduces inventory complexity. |
Summary: Using Type B thermocouples in zirconia oxygen sensors ensures high-temperature performance, low drift, precise trace oxygen measurement, and long-term reliability. Type K is suitable for conventional temperature ranges but has lower stability and precision under demanding industrial conditions.
Product datasheet: O2 Analyzer(Zirconia principle) ![]() , if you need more information, please contact us at sales@mzdd.de.
, if you need more information, please contact us at sales@mzdd.de.
Measurement components and ranges
• O2: 0 ~ 100 / 1000ppb
0 ~ 1 / 10 / 1000ppm
0~ 1% / 10% / 25% / 100%
Glove boxes, oxygen analyzer, Welding and soldering, Semiconductor, Heat and surface treatment,Combustion plants, porcelain and ceramic firing, Vacuum process control, industrial plasma processes, Test gas generator for laboratory equipment
