The principle and selection precautions of trace moisture analyzer in gas
1. Basic concepts
1.1 Humidity
In the measurement law, humidity is defined as the "quantity of the state of the object". Normally refers to the proportion of water contained in a certain substance.
Absolute humidity: The mass (g) of water vapor per unit volume (1m3) of gas.
Relative humidity: The ratio of the water vapor pressure (E) in the gas to the saturated water vapor pressure (Es) of the gas, expressed as a percentage: RH=E/Es×100%.
The humidity referred to in daily life is relative humidity.
1.2 Saturated water vapor pressure
The amount of water vapor in the gas is limited, and the state that reaches the limit is called saturation, and the water vapor pressure at this time is called the saturated water vapor pressure.
1.3 Dewpoint
Gases at different temperatures have different qualities of water vapor. A gas with a higher temperature also contains more water vapor. The saturated water vapor pressure corresponding to each temperature is constant. When a certain volume of gas is uniformly cooled under a constant pressure, the partial pressure of the gas and the moisture in the gas remains unchanged, the quality of the water vapor does not change, and the relative humidity increases, when it drops to a certain temperature Td When the relative humidity RH reaches 100% saturation, at this time, if the cooling is continued, until the moisture in the gas reaches a saturated state, part of the water vapor will condense into dew. The temperature at this time is the temperature at which the number of water molecules in the gas reaches dynamic equilibrium to determine the dew point of the gas, which is the dewpoint temperature, that is, the dewpoint temperature. If the dew point freezes below 0℃, it is the Frost Point.
The relative humidity is obtained from the dew point according to temperature and pressure to indirectly measure moisture, but it is greatly affected by pressure and temperature. Therefore, it is divided into normal pressure dew point and pressure dew point, and they can be interchanged.
1.4 How to express humidity
It is expressed as the dew point temperature value in ℃. It is expressed as the ratio of the sub-volume of water vapor in the wet gas to the sub-volume of dry gas, in ppm (v). Expressed by the mass of water vapor per unit volume of moisture, in g/m3.
Conversion between values in different representation methods. For example: the dew point value is -40℃=126.8ppm=0.09491g/m3.
1.5 Conversion table of dew point, humidity and ppm
Dew point ºC | Saturated vapor pressure mmHg | Relative humidity % | g/Kg | ppm |
-100 | 0.0000099 | 0.000053 | 0.0081 | 0.013 |
-98 | 0.000015 | 0.00008 | 0.012 | 0.0197 |
-96 | 0.000022 | 0.00012 | 0.018 | 0.0289 |
-94 | 0.000033 | 0.00018 | 0.027 | 0.4034 |
-92 | 0.000048 | 0.00026 | 0.039 | 0.0632 |
-90 | 0.00007 | 0.00037 | 0.05 | 0.0921 |
-88 | 0.0001 | 0.00054 | 0.082 | 0.132 |
-86 | 0.00014 | 0.00075 | 0.11 | 0.184 |
-84 | 0.0002 | 0.00107 | 0.16 | 0.263 |
-82 | 0.00029 | 0.00155 | 0.24 | 0.382 |
-80 | 0.0004 | 0.00214 | 0.33 | 0.526 |
-78 | 0.00056 | 0.003 | 0.46 | 0.737 |
-76 | 0.00077 | 0.0041 | 0.63 | 1.01 |
-74 | 0.00105 | 0.00559 | 0.86 | 1.38 |
-72 | 0.00143 | 0.00762 | 1.17 | 1.88 |
-70 | 0.00194 | 0.0104 | 1.58 | 2.55 |
-68 | 0.00261 | 0.014 | 2.13 | 3.43 |
-66 | 0.00349 | 0.0187 | 2.84 | 4.59 |
-64 | 0.00464 | 0.0248 | 3.79 | 6.11 |
-62 | 0.00614 | 0.0328 | 5.01 | 8.08 |
-60 | 0.00808 | 0.043 | 6.59 | 10.6 |
-58 | 0.0106 | 0.0565 | 8.63 | 13.9 |
-56 | 0.0138 | 0.0735 | 11.3 | 18.2 |
-54 | 0.0178 | 0.0948 | 14.5 | 23.4 |
-52 | 0.023 | 0.123 | 18.8 | 30.3 |
-50 | 0.0295 | 0.157 | 24.1 | 38.8 |
-48 | 0.0378 | 0.202 | 30.9 | 49.7 |
-46 | 0.0481 | 0.257 | 39.3 | 63.3 |
-44 | 0.0609 | 0.325 | 49.7 | 80.8 |
-42 | 0.0768 | 410 | 62.7 | 101 |
-40 | 0.0966 | 0.516 | 78.9 | 127 |
-38 | 0.1209 | 0.644 | 98.6 | 159 |
-36 | 0.1507 | 0.804 | 122.9 | 198 |
-34 | 0.1873 | 1 | 152 | 246 |
-32 | 0.2318 | 1.24 | 189 | 305 |
-30 | 0.2859 | 1.52 | 234 | 376 |
-28 | 0.351 | 1.88 | 287 | 46.2 |
-26 | 0.43 | 2.3 | 351 | 566 |
-24 | 0.526 | 2.81 | 430 | 692 |
-22 | 0.64 | 3.41 | 523 | 842 |
-20 | 0.776 | 4.13 | 633 | 1020 |
-18 | 0.939 | 5 | 770 | 1240 |
-16 | 1.132 | 6.03 | 925 | 1490 |
-14 | 1.361 | 7.25 | 1110 | 1790 |
-12 | 1.632 | 8.69 | 1335 | 2150 |
-10 | 1.95 | 10.4 | 1596 | 2570 |
-8 | 2.326 | 12.4 | 1900 | 3060 |
-6 | 2.765 | 14.7 | 2260 | 3640 |
-4 | 3.28 | 17.5 | 2680 | 4320 |
-2 | 3.88 | 20.7 | 3170 | 5100 |
0 | 4.579 | 24.4 | 3640 | 6020 |
2 | 5.294 | 28.2 | 4330 | 6970 |
4 | 6.101 | 32.5 | 4990 | 3030 |
6 | 7.013 | 37.4 | 5730 | 9230 |
8 | 8.045 | 42.9 | 6580 | 10590 |
10 | 9.209 | 49.1 | 7530 | 12120 |
12 | 10.52 | 56.1 | 8600 | 13840 |
14 | 11.99 | 63.9 | 9800 | 15780 |
16 | 13.63 | 72.6 | 11140 | 17930 |
18 | 15.48 | 82.5 | 12650 | 20370 |
20 | 17.54 | 93.5 | 14330 | 23072.37 |
2. Common Moisture Analyzer Detection Principles
2.1 Coulometric method (Electrolysis):
The Coulometric moisture analyzer was successfully tested by Keide in 1959 and applied to low-content moisture measurement. Belongs to the absolute value of the direct measurement of moisture!
The sensor pillar is plated with parallel spiral platinum layer as the electrode, and the hydrated phosphorus pentoxide film is coated between the platinum layer. Phosphorus pentoxide has a strong water absorption, when chlorine gas flows steadily through the sensor flow cell, where the water is absorbed to generate phosphoric acid, the reaction formula is as follows:
P2O5 + 3H2O → 2H3PO4
At the same time, between the two platinum layers to plus DC voltage, that has the electrolysis reaction, phosphoric acid is reductively decomposed into oxygen,chlorine, phosphorus pentoxide.The reaction formula is as follows:
4H3PO4→6H2+3O2+2P2O5
When the absorption and electrolysis reach a balance, the water entering the electrolytic cell is absorbed by the phosphorus pentoxide film and electrolyzed. According to Faraday's law of electrolysis and gas law, it can be deduced that the electrolysis current of water is proportional to the water content of the gas sample. The specific calculation relationship is as follows:
I = QPT0FU×10-4/3P0TV0
I-electrolysis current of water, μA;
U-water content of the gas sample μL/L (volume ratio);
Q-gas sample flow mL/min;
P—environmental pressure, Pa;
T0=273.15K;
F=96485C;
P0=101325 Pa;
T—the absolute temperature of the environment, K;
V0=22.4L/mol.
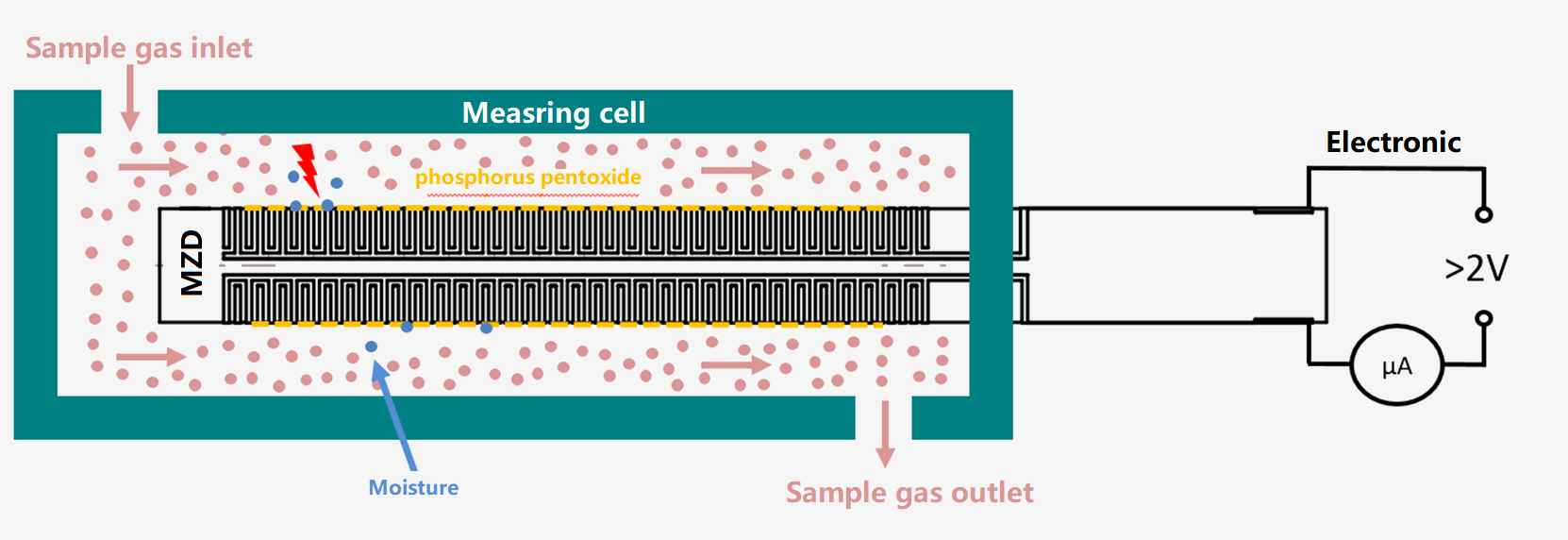
The electrolysis moisture analyzer is an absolute measurement method, which is stable and does not drift. It can be used for acid gas such as chlorine, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen sulfide, hydrogen fluoride, sulfur dioxide, sulfur trioxide, or used for air, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, argon, helium, neon, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, sulfur hexafluoride , Methane, ethane, propane, butane, natural gas and other neutral gases, but not suitable for alkaline gases that react with P2O5, such as ammonia.
The phosphorous pentoxide coating needs to be regenerated regularly, and the maintenance cost is very low, usually using phosphoric acid regeneration every 3 to 6 months. When used in high-humidity situations, the life of the phosphorus pentoxide coating will be shortened, and the regeneration cycle needs to be shortened.
2.2.1 Glass pillar sensor
Wrap the positive and negative electrode platinum wires on the outer or inner wall of the glass cylinder.
2.2.2 Ceramic pillar sensor
Based on the glass sensor, MZD have developed a ceramic sensor that can realize standardized and automation production. Positive and negative platinum layers are plated on ceramic flat plates. The contact area between the platinum layer and the sample gas is larger, the reaction is faster, and the measurement is more stable and reliable.
2.2 Laser method:
Pass the light of a certain wavelength range through the sample gas, and compare the detected spectrum with the reference spectrum, so that some relative changes or absorption of certain wavelengths of the spectrum will be measured. The absorption is proportional to the moisture content in the sample gas. The gas composition needs to be clean, the small range is 0-10ppm, the accuracy is high, and it can be used in the electronics industry; the large range is 0-2000ppm, but the accuracy is 100ppm. Not suitable for occasions contaminated by impurity particles.
2.3 Optical fiber method:
The surface of the fiber optic humidity sensor is a laminated structure composed of silicon oxide and zirconium oxide with different reflection coefficients. Through advanced thermal curing technology, the aperture of the sensor surface is controlled to 0.3nm, and water molecules of 0.28nm can penetrate. The controller emits a beam of near-infrared light of 790~820nm, which is transmitted to the sensor through an optical fiber cable. The water molecules entering the sensor will change the reflection coefficient of the light, thereby causing a change in wavelength, and the amount of change corresponds to the moisture content of the medium. The proportional relationship. By measuring the wavelength of the received light, the dew point and moisture content of the medium can be obtained. High precision, maintenance-free, very stable, can measure corrosive media containing H2S, HCL, etc.; the transmission fiber is easy to break and needs to be protected, and it is not suitable for occasions contaminated by impurity particles.
2.4 Dew point method
The relative humidity is obtained from the dew point according to temperature and pressure to indirectly measure moisture, but it is greatly affected by pressure and temperature. Therefore, it is divided into normal pressure dew point and pressure dew point, and they can be interchanged.
2.4.1 Chilled Mirror Method
When the gas to be measured enters the detection chamber under constant pressure, it passes the mirror at a certain flow rate. When the temperature of the mirror is higher than the dew point temperature of the gas, most of the incident dry mirror light is reflected to the photodetector, and is controlled by an amplifier and cooling. Reduce the temperature of the mirror surface. When the temperature of the mirror surface is lower than the dew point temperature of the gas, the incident light is diffusely reflected on the mirror surface due to condensation or frost, and the signal of the photodetector is weakened. Through the amplifier, the heating side is controlled to reduce the cooling capacity. Finally, the mirror temperature is automatically balanced on the dew point of the sample gas, and the temperature of the mirror at this time is measured by the thermal resistance element as the dew point temperature.
2.4.1.1 The measurement is accurate, stable and no drift, the highest accuracy instrument can reach ±0.3℃.
2.4.1.2 The price is higher, the requirements for operators are higher, and maintenance is required.
2.4.1.3 Sometimes there is supercooled water in the range of -20℃~0℃, and the cold mirror method cannot distinguish between the ice deposited on the mirror surface and the supercooled water, because the water vapor pressure is different from the ice vapor pressure, when the mirror is cooled Below 0ºC, ice may form immediately or depending on the cleanliness of the mirror and gas, even before it becomes ice at minus 44 Cº, it may be super-cooled water. This means that the readings of the instrument may have errors of up to 4 degrees Celsius. Therefore, the accuracy claimed by the cold mirror manufacturer (±0.2ºC) is absurd! Therefore, be especially careful to distinguish between cold water and frost.
2.4.1.4 The sample gas needs to be clean, sensitive to pollutants, and not resistant to corrosion. It is not suitable for occasions with impurity particles pollution and corrosiveness.
2.4.1.4.1 When there are water-soluble substances on the mirror surface, the equilibrium vapor pressure at this time will be lower than the saturated vapor pressure of pure water without impurities, which will make the measured dew point temperature higher than the actual sample gas dew point temperature, which is called Lawu Seoul effect.
2.4.1.4.2 When there are non-water-soluble impurities on the mirror surface, the background scattering level of the mirror surface will be changed, resulting in zero point shift.
2.4.1.5 When condensation is formed on the metal surface, due to the effect of surface tension, the saturated water vapor pressure on the curved surface of the lens will increase, which will make the measured dew point temperature lower than the actual sample gas dew point temperature, which is called the Kelvin effect . In the actual measurement of dew point, the Kelvin effect and the Raoul effect are just opposite, and they will cancel each other out. But the influence of the Raoult effect is much greater than the Kelvin effect, because water-soluble impurities inevitably exist in the mirror and the gas to be measured more or less, and the impurities in the gas may sometimes be related to the water-insoluble substances on the mirror. A chemical reaction or a photochemical reaction occurs, and it is converted into a soluble substance.
2.4.1.6 In the actual working process of the instrument, the mirror surface does not start to condense uniformly. The condensation layer always appears on a certain area of the mirror surface first. It is probably due to the flaws such as scratches on the mirror surface. The remaining substances are not easy to remove. On the other hand, the edges and corners of defects act as "nucleus" and accelerate the condensation process.
2.4.2 Capacitance method
Dew point meter for measuring relative humidity. Usually the measurement range is -60~20 °C, and the lowest can be measured at −80 °C.
Dew point meter for measuring absolute humidity. Usually the measurement range is -100~20 °C, and the lowest can measure -120 °C.
The capacitive dew point method is an indirect measurement of moisture. It is cheap and not resistant to corrosion. Operation at higher temperatures or certain gases will cause drift. It must be calibrated regularly to eliminate aging, lag and pollution, and post-maintenance costs are high! When the moisture content of the sample gas will be less than 10ppm for a long time, a dew point meter that measures absolute humidity should be selected.
2.4.2.1 Film capacitance sensor
The thin film sensor is depositedon two conductive electrodes, about 1~10μm thick polyamine salt or cellulose acetate polymer film, when the film absorbs or loses water, it will change the dielectric constant between the two electrodes, thereby measuring Dew point. Some high temperature resistant thermosetting polymer sensors can continuously measure high humidity and moisture at 200°C.
The thin film sensor measures the dew point by measuring the relative humidity, so its measurement range is wide, and the dew point measurement range can reach -50℃~100℃. Since all relative humidity sensors are sensitive to temperature, if they are calibrated at one temperature, they will cause errors when used at different temperatures. Although the polymer sensor is less dependent on temperature, the error is smaller when the operating temperature is different from the calibration temperature. The accuracy can reach ±1%RH in a very narrow range, and it can reach ±3%RH in a wide range of temperature and humidity. But for occasions with higher accuracy requirements, temperature compensation is required.
The thin film sensor has fast response, wide temperature and humidity measurement range, good linearity, good stability and repeatability, low temperature coefficient, low cost, and needs regular calibration. It is usually used in medium and high temperature and humidity occasions. It is not recommended to use in low humidity below 10ppm occasion.
2.4.2.2 Alumina Capacitance Sensor
The capacitance sensor is composed of an aluminum plate separated by a layer of aluminum oxide (AL2O3) and a layer of gold to form two positive and negative plates. When gas passes through the sensor, the moisture absorption layer of aluminum oxide causes a change in capacitance. At this time, the impedance of the capacitor is proportional to the partial pressure of water vapor. The partial pressure of water vapor can be obtained by measuring the impedance or capacitance of the capacitor, and the dew point value can be obtained by conversion.
The accuracy of capacitance sensor in the middle and high humidity range is generally ±1~±2℃; in the low humidity range, its accuracy is generally ±2~±3℃. This type of sensor is not resistant to corrosion. Although it does not react with hydrocarbon gases, CO, CO2, and chlorofluorocarbon gases, it will have different drifts for different gases.
2.5 Quartz Crystal Method (QCM)
After the surface coating of the quartz crystal with hygroscopic coating absorbs a certain amount of moisture, the resonant frequency of the quartz crystal decreases due to the increase in mass, so the change in the resonant frequency of the quartz crystal reflects the change in moisture. Quartz crystal vibration moisture analyzer can be used to measure the moisture content (ppbV and ppmV) of industrial pure gas, and its measurement is reliable, fast and accurate.
3. Measuring method of trace moisture in different kinds of gases
No | Industry | Product | Measuring | Measuring method | Note |
1 | Industial gas | liquid oxygen | moisture | Weight | |
2 | SF6 | moisture | Weight, Coulometric, Dewpoint | Weight prciple is standard | |
3 | Ethylene | moisture | Karl-Fischer, Hygrometer(Piezoelectric, Coulometric and capacitive) | ||
4 | Propene | moisture | Karl-Fischer Coulomb, Hygrometer(Piezoelectric and capacitive) | ||
5 | Butadiene | moisture | Karl-Fischer | ||
6 | Difluorochloromethane | moisture | Karl-Fischer | ||
7 | Isobutane | moisture | Karl-Fischer, Coulometric | Karl-Fischer principle is standard | |
8 | Isobutane | moisture | Karl-Fischer | ||
9 | Industial gas or Semiconductor gas | Nitrogen Trioxide | moisture | Piezoelectric, Coulometric | Coulometric standard |
10 | SF6 | moisture | Coulometric, Dewpoint | ||
11 | Chlorine | moisture | Coulometric | Coulometric is standard | |
12 | Silane | moisture | Coulometric | Coulometric is standard | |
13 | Phosphine | moisture | spectroscopy | pectroscopy principle is standard | |
14 | Picarro | moisture | spectroscopy | Spectroscopy principle is standard | |
15 | Ammonia | moisture | Dewpoint | Dewpoint is standard | |
16 | Hydrogen oxide | moisture | Dewpoint | ||
17 | Hydrogen | moisture | spectroscopy | Spectroscopy principle is standard | |
18 | Oxygen | moisture | spectroscopy | Spectroscopy principle is standard | |
19 | Nitrogen | moisture | spectroscopy | Spectroscopy principle is standard | |
20 | Helium | moisture | Coulometric | Coulometric is standard | |
21 | Argon | moisture | Coulometric | Coulometric is standard | |
22 | Medical gas | Oxygen | moisture | Dew-Point, Coulometric | Coulometric is standard |
23 | Ammonia | moisture | Weight, Coulometric, Dew-Point | Weight principle is standard | |
24 | Argon | moisture | Coulometric, Dewpoint | Dewpoint is standard | |
25 | High purity Argon | moisture | Coulometric, Dewpoint | Dewpoint is standard | |
26 | purity Ammonia | moisture | Coulometric | ||
27 | High purity Ammonia | moisture | Coulometric | ||
28 | Neon | moisture | Coulometric, Dewpoint | ||
29 | Methane | moisture | Coulometric | ||
30 | Oxygen | moisture | Coulometric | Coulometric is standard | |
31 | Ammonia | moisture | Coulometric, Dewpoint | Dewpoint is standard | |
32 | Hydrogen | moisture | Dewpoint | ||
33 | Xenon | moisture | Coulometric, Dewpoint | Dewpoint is standard | |
34 | Krypton | moisture | Coulometric, Dewpoint | Dewpoint is standard | |
35 | Natural gas | moisture | Dewpoint | ||
36 | Dimethyl ether | moisture | Karl-Fischer Coulomb, Coulometric, Karl-Fischer Volumetric | Karl-Fischer Coulomb(Flash injection sample) is standard |
