
Direct measurement of NO2
PAS-photoacoustic spectroscopy
PHOTO Acoustic Spectroscopy (PAS) is a spectroscopic method that utilizes the photoacoustic effect. The method has been proven in a variety of applications such as vehicle emission testing, environmental technology (detection of air pollutants), medical technology and biology.
It is a highly accurate, stable and direct measurement (independent of the background gas).
It is based on the fact that light is absorbed by gas molecules. In photoacoustic spectroscopy, modulated light is converted into sound waves. The resulting acoustic wave is converted into an electrical signal using a microphone.
Performance of PAS (NO 2) sensors:
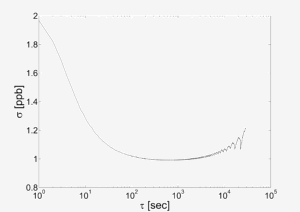
Allen variance
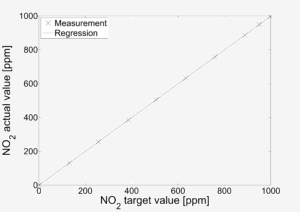
Linearity
The sample gas is irradiated with a modulated light of a predetermined wavelength. This is because for many applications, the specific wavelength of the material under examination is in the infrared range. Therefore, infrared laser diodes are used as light sources. The light is electronically or mechanically modulated, for example, by using a chopper.
When the light frequency corresponds to the absorption band of the gas in the cell, the gas molecules absorb part of the light. The higher the concentration of the gas, the more light is absorbed.
The absorbed light leads to heat and therefore to an increase in pressure. Due to the modulated light, the pressure will alternately increase and decrease.
This will produce an acoustic signal which can be detected by the microphone and then converted into an electrical signal.
The main advantage of the photoacoustic effect is that the sensitivity does not depend essentially on the length of the light range.
This enables high sensitivity from short absorption path lengths and a highly linear concentration response over a wide dynamic measurement range at very low sample volumes.
Extremely accurate results with no interfering signals
Absorbance is measured directly, independent of background.
As a result, PAS is one of the most sensitive methods for detecting gases and is commonly used for trace gas analysis.
Small sample size, small cell size
The small size of the PAS cuvette allows the measurement of very small amounts of gases.
This allows for a significant reduction in sample volume compared to conventional methods.
Low drift
The response of the microphone is very stable. Therefore, the drift is very small and calibration is hardly required.
